Proxy vs VPN: What Are the Differences?
We reveal the strengths and weaknesses of each.
You’ve probably seen the phrase “Virtual Private Network” (VPN) thrown about everywhere by now: protect your privacy this, hide your identity that, unblock videos, etc. You might have also heard or read the term “proxies” somewhere.
But how different are these tools? Which one is for protecting your online identity? Which one gives you access to geo-blocked content? The questions just keep piling on.
Don’t worry, we’re here to provide the answers. In this article, we’ll look at the differences between a proxy vs a VPN and try to find out which one is better.
Let’s begin by taking a quick look at what proxies and VPNs are. If you prefer a video, we have one as well.
Proxies and VPNs: What Are They?
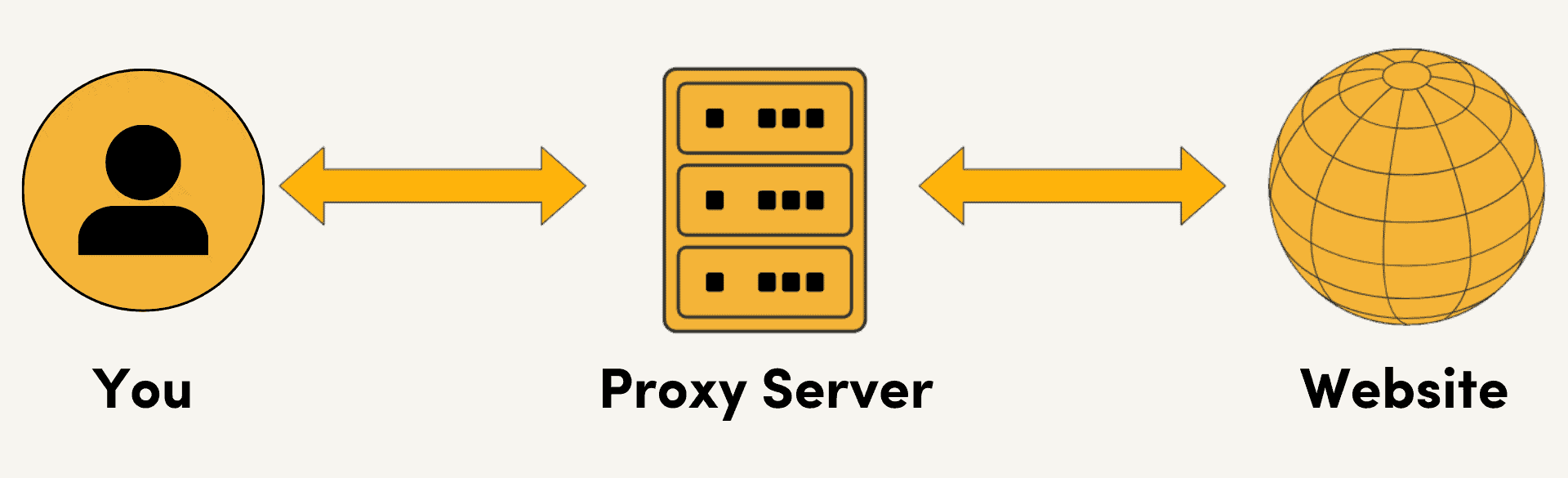
A proxy server is an intermediary between you and the internet. Instead of connecting to a website directly, you connect to a proxy server first. All of your requests to the target are then routed through the proxy server, and any replies go through that same server as well.
Naturally, to be able to act as a digital middleman, the proxy server has its own IP address. And for the target website, that proxy IP address is YOUR address. Meanwhile, your true IP remains hidden, known only to the proxy server.
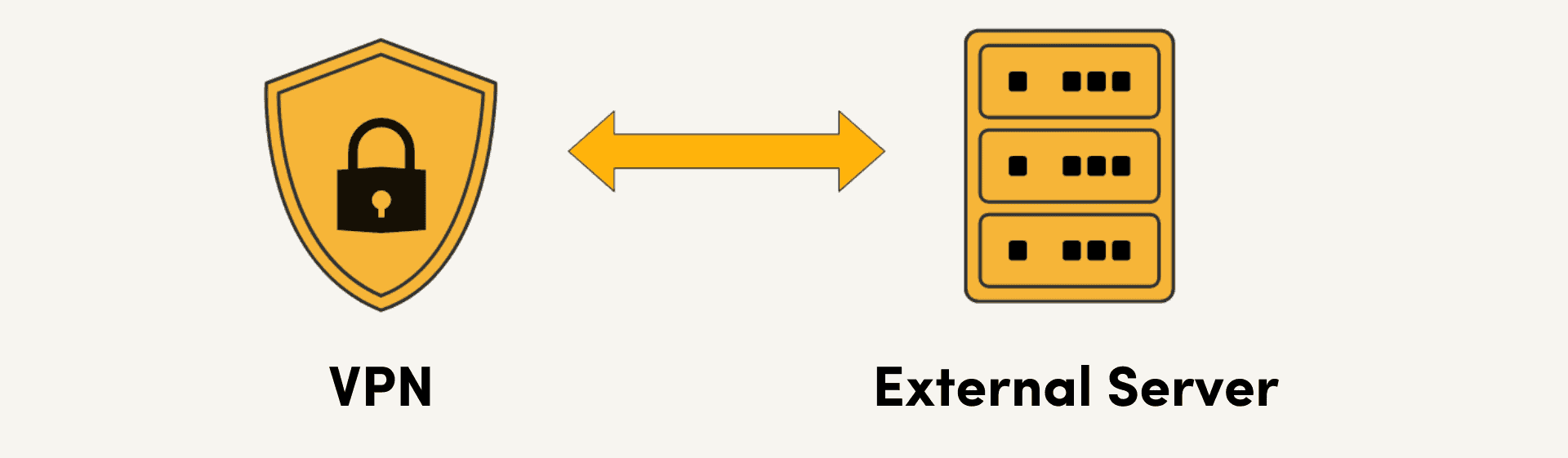
A VPN also serves like an intermediary, just like a proxy does. The big difference is that all the data between your device and the VPN server is encrypted. This way, a so-called VPN tunnel is established. Anyone eavesdropping on your connection will only see scrambled data passing between your device and the VPN server -– the contents or where the data is going remain hidden.
Are There Any Similarities?
Indeed, there are quite a few similarities between the two:
- Both proxies and VPNs improve your privacy online – by using them, you present a different IP address to websites and services. That way, you can browse the web and use apps while keeping your own IP hidden. So while true anonymity is impossible as you will be leaving a digital footprint somewhere, it will help you improve your privacy online.
- Both proxies and VPNs overcome website and geo-location restrictions – you can access websites restricted at your work, school, or even your country when you route your traffic through a proxy or VPN. For example, you can unblock Instagram. Many people also use VPNs to access popular websites like YouTube or Netflix. Both options can give you an IP address from any country in the world, which lets you browse like a local.
Are There Any Differences?
Yes, and important ones at that:
- VPNs work at the operating system level; proxies are app-based – what does that mean? When you connect to a VPN server, it will affect all your connections, no matter which app you use. Proxies, on the other hand, work at the application level – they only affect the traffic from apps configured to use them.
- Proxies allow making many connections at once – you can buy hundreds of proxy IPs at once – and more. Many residential proxy providers can give you access to pools with millions of IP addresses. This is vital for many commercial activities like web scraping and other bulk tasks. VPNs, on the other hand, are best suited for personal use, improving online security and privacy. This is perhaps the biggest difference between the two, and one that clearly distinguishes a proxy from a VPN.
- VPNs don’t hide the fact that you’re using a VPN – while a VPN might make you anonymous in the eyes of websites and even your Internet Service Provider (ISP), it doesn’t try to hide the fact that you’re connected to a VPN server. A residential proxy server makes the target think that the data is coming from a real person. This distinction is, most of the time, not important. However, it can become vital if a service blocks VPNs or in certain use cases like ad verification and sneaker copping.
- VPNs encrypt your data – encryption is at least half the reason for using a VPN, as any data passing between your device and the VPN server will be turned into an unreadable mess. This is less important with mass adoption of the HTTPS standard, but if you’re worried about someone intercepting your data before it reaches the VPN, this is what you need. Meanwhile, proxies don’t encrypt data by default, though they can be configured in a way that would allow it.
Proxy vs VPN: Which Is Faster?
It depends on the type of proxy! A datacenter proxy server will most likely be faster than a VPN. Such proxy servers are hosted in powerful data centers – just like VPNs. But proxies don’t use such sophisticated encryption, so the encryption overhead – bandwidth required just for encryption purposes – is lower.
A residential proxy will be slower than a VPN. Residential proxies are rented out from real people with real devices – and this means the connections can be at times slow and/or unstable.
Proxy vs VPN: Which Is More Secure?
Once again, it depends! HTTP proxies aren’t secure, and a skilled hacker can steal the data you send through them. But as long as you use a reliable provider and SOCKS5 or HTTPS proxies, they’re generally safe (remember to never use free proxies!)
Still, connecting through a VPN server is undoubtedly more secure. A respectable VPN will use one or several encryption protocols like OpenVPN, IPSec, and Wireguard and have additional security features, such as an automatic kill-switch.
However, as with proxies, you need a reliable VPN provider – so free VPNs are a no-go, as they have both the incentives and power to profit off your data.
So, Which Is Better: VPN or Proxy?
It really depends on what you’re trying to achieve. If you only want to improve your security online or unblock content, a VPN will generally be a better choice. But if you need to do bulk tasks that involve automation, proxies will be much better suited for that.

Frequently Asked Questions About Proxy Servers vs VPNs
A premium VPN provided by a trustworthy company is the superior option for this use case – and will give you fewer headaches.
Yes, but the benefits are questionable. Both of them hide your real IP address online, so outside of scenarios where you trust only one of the providers (proxy or VPN) and don’t want them to know your IP, doubling up has limited use. In fact, having both tools working at the same time can seriously degrade your connection speed and quality.
As a general rule: use a VPN when you need one secure connection; use a proxy when you need many connections at once. For example, a VPN is better for protecting your connection, but is absolutely unsuited for tasks like web scraping.